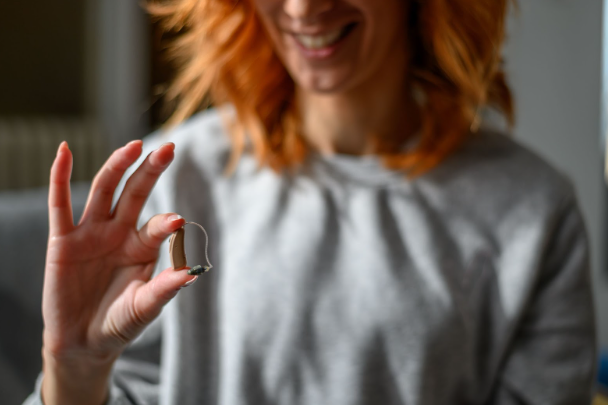
Everything You Need To Know About Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids
Learn what OTC hearing aids are, their benefits, audiologists' opinions on them, and more in our insightful article. Click here to read more!

Did you know the cost of hearing aids can often reach an average of $2,500 per device? After years of anticipation, FDA-regulated over-the-counter hearing aids are finally available, promising to make hearing aids more accessible and affordable for those experiencing hearing loss.
In response to consumer and government agencies' demands for affordable and accessible hearing aids in the United States, over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids are now available starting at $500. They’re still a sizeable investment but less than many prescription hearing aids.
With OTC hearing aids, individuals experiencing mild to moderate hearing loss can take control of their hearing health without needing costly appointments and prescriptions.
The availability of hearing aid technology through OTC options represents a significant step forward in ensuring everyone can reap the benefits of these devices.
If you're in the market for OTC hearing aids, here's what you need to know.
What Are OTC Hearing Aids?

A hearing aid is a medical device used for hearing assistance worn behind or within the ear canal. While traditional hearing aids require a doctor's or audiologist's prescription, over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids can be purchased directly by consumers without needing a prescription or professional fitting.
That means people experiencing hearing loss can bypass the formal hearing evaluation, fittings, or prescription costs by purchasing hearing aids at their convenience.
Does Insurance Cover Hearing Aids?
Coverage for hearing aids varies between insurance companies and plans. Some insurances provide coverage for prescription hearing aids, and some private insurance plans cover all or some portion of the total expense of hearing aids. Some offer it as a separate benefit, like vision or dental coverage.
Healthcare laws in 20 states require insurance companies to pay for hearing aids for children, but only five states mandate insurance coverage of hearing aids for adults, including Arkansas, Connecticut, Illinois, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island.
Several OTC hearing aid companies, like Eargo and MDHearing, are working with insurance companies to increase coverage for OTC hearing aids.
Buying hearing aids without insurance can be done through government benefits, discounts for members of national organizations, and using tax-free dollars and payment plans. Some methods include AARP hearing aid discounts, FSA (Flexible Spending Account) or HSA (Health Savings Account), discounts for government employees, veteran benefits, and financing and subscription plans.
Prescription Hearing Aids vs. OTC Hearing Aids
Hearing aids and OTC devices work the same way. Both pick up sounds with small microphones, amplify them, and transmit them to your ear via a speaker. The most significant difference between OTC and hearing aids is the need for a hearing evaluation, a prescription and assistance to program them accordingly, including 'fittings' and follow-up adjustments as needed.
With OTC hearing aids, there's no requirement to visit a specialist or have a hearing test before buying a device, and setting up the hearing aid is up to you.
The FDA regulates OTC hearing aids to ensure safety and efficacy, and they can be purchased at pharmacies, electronics stores, or online.
OTC Hearing Aids:
- Do not require implantation or other surgical intervention.
- Are approved for adults 18 years or older.
- Are intended to help with mild to moderate hearing loss, not for those with severe hearing loss.
- Allow users to customize the device settings to their hearing needs.
- Do not require a hearing exam or prescription.
Who are OTC hearing aids for?
OTC hearing aids are for adults (18 and older) who believe they have mild to moderate hearing loss, even if they have not had a hearing exam. They are not intended for children. Children need prescription hearing aids for their growth and development and new earpieces as they grow.
What Are the Benefits of OTC Hearing Aids?
Hearing aids are an expensive purchase, and for many people experiencing hearing loss, financing them can mean the difference between addressing their hearing loss and delaying treatment.
OTC hearing aids facilitate access and early intervention for people with hearing loss. Users can conveniently purchase over-the-counter hearing aids at retail stores or online, reducing the wait time to asses hearing loss and fit hearing aids.
At the same time, OTC hearing aids empower individuals to take control of their hearing needs and make choices independently.
The hearing aid devices are easy to use and have user-friendly features such as pre-programmed settings and volume control.
What to Know Before Buying OTC Hearing Aids?
Before purchasing OTC hearing aids, it’s important to be well-informed and understand your needs. There's much to consider, from the degree of hearing loss to safety standards and pricing options.
While OTC hearing aids offer several advantages, they may not suit everyone. OTC hearing aids are limited in their maximum output and may not be adequate to treat severe or profound hearing loss, as they may not provide appropriate hearing benefits.
OTC hearing aids are designed for people with mild to moderate hearing loss, but it is also important to consider your long-term needs and determine if this is a suitable solution for your specific hearing requirements and lifestyle.
What Are the Symptoms of Mild to Moderate Hearing Loss?

Symptoms that suggest mild to moderate hearing loss are:
- Difficulty hearing speech in noisy places.
- Tinnitus - a persistent ringing, buzzing, or hissing sound in the ears.
- Trouble hearing on the phone.
- Conversation fatigue - communication can become tiring due to increased effort to hear and understand.
- Turning up the volume on the TV, radio, or other audio devices - noticed by others in the household.
- Reduced awareness of environmental sounds.
Although these symptoms may vary from person to person and may progress over time, people with mild to moderate hearing loss are good candidates for OTC hearing aids.
Before purchasing an OTC hearing aid, ensure the brand you select offers a trial period and a customer service support line if you need assistance with fitting or proper functioning.
What to Know After Buying OTC Hearing Aids?
OTC hearing aids provide fitting and setting instructions, including managing a volume control or app-based program to personalize the device for your specific needs and preferences.
It’s important to note that even though these devices are straightforward and simple to operate daily, they take time and practice to get used to.
To become familiar with them, here are a few tips:
- Wear them regularly: The more you wear your hearing aids, the faster you adjust and the more natural it will become.
- Start slowly: Gradually increase the time you wear them each day to allow you to get used to new sounds.
- Explore their features: Practice listening, conversing, and fine-tuning the settings according to your preferences.
- Seek support: Talk to family members or consult a physician to discuss challenges and opportunities for improvement.
What Do Audiologists Think of OTC Hearing Aids?
While some audiologists view OTC hearing aids as a valuable solution for addressing a noticeable gap in hearing healthcare, offering a more cost-effective and accessible option that can serve as a crucial initial step for individuals who might otherwise neglect their mild to moderate hearing loss, there are also those within the profession who underscore the vital necessity of a thorough hearing evaluation.
This evaluation ensures the accurate diagnosis of the type and extent of hearing loss, evaluating potential concerns regarding the safety and effectiveness of OTC hearing aids.
Here are some potential concerns regarding OTC hearing aids:
- Individuals are not trained to accurately assess their hearing loss level.
- Lack of knowledge to address hearing aid malfunctions.
- Lack of guidance for maintenance best practices.
- Improper fitting of the device.
- Not addressing moisture and wax issues.
- Self-diagnosis may lead to potentially missing underlying conditions that can affect hearing.
Conclusion
If you’re experiencing symptoms of hearing loss, consider discussing your needs with an audiologist or health care provider. OTC hearing aids are still considered to be in their early release stages. Therefore, invest in a solution most supportive of your needs.
We hope this can help you decide if you should opt for a traditional hearing aid or an over-the-counter device, which is more accessible.