How AI Is Improving Accessibility For Deaf and Hard of Hearing Communities
AI-powered solutions play a significant role in reshaping accessibility for deaf and hard of hearing communities. Read this article to learn more about it!

AI-powered solutions play a significant role in reshaping accessibility for deaf and hard of hearing communities, specifically in how we consume media and communicate with others in person and online.
As we explore the intersection of AI and accessibility, we see that the potential for positive change is boundless. This includes educational and professional opportunities, breaking daily communication barriers, and fostering inclusivity.
In this article, we look at some remarkable ways AI transforms accessibility.
The Current State of AI and Its Impact on Accessibility
AI has made media and communication more accessible than ever. Thanks to FCC regulations, traditional video program distributors, including cable operators and broadcasters, have made significant strides in providing closed captioning for TV programs. This ensures that individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing can access televised content.
However, there’s still a growing need for proper captioning in online media, especially on major digital channels like YouTube, Instagram, and other social media platforms. Also, challenges persist in customer service centers that rely solely on phone interactions or automated systems, which can be inaccessible to individuals who need help navigating these systems using voice commands.
Nevertheless, there are promising opportunities, with the potential for AI-driven features such as speech-to-text, text-to-speech, and improved speech recognition.
Speech Recognition and AI
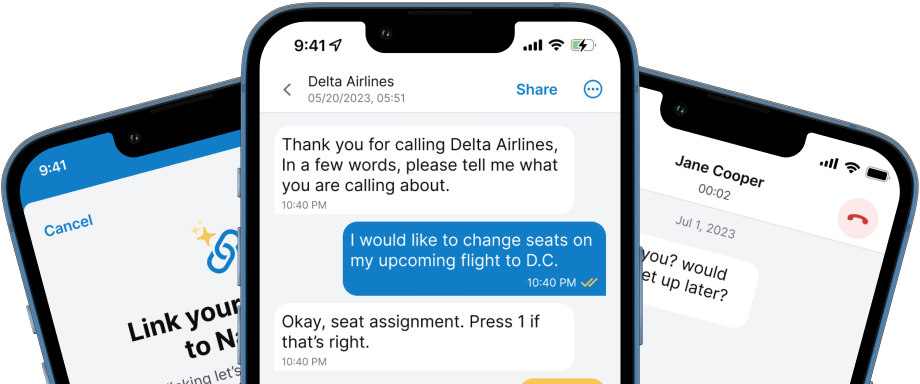
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) and auto-generated captions convert spoken language into text for in-person, phone, and video platforms. This technology has different applications across various sectors. Some of the most common uses of ASR include phone call centers, healthcare settings, educational institutions, and online platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube, allowing viewers who are deaf and hard of hearing to enjoy the content.
As technology advances and improves accuracy, phone calls and in-person conversations are seamlessly transcribed, becoming more easily accessible for deaf and hard of hearing individuals. Applications like Nagish are a great example of this use case, capturing the world around you in real-time into written text to make day-to-day interactions accessible.This includes phone conversations, class lectures, one-on-one interactions, public announcements, and much more.
How AI is Shaping the Future of Sign Language
Sign language is a visual language. With signing, the brain processes linguistic information through the eyes. The shape, placement, and movement of the hands, facial expressions, and body movements all play important parts in conveying information. It is used primarily by deaf and hard of hearing individuals. There is no universal sign language, as each is based on the unique dialect and culture of the region from which it originates.
Like any spoken language, ASL (American Sign Language), for example, is a language with its own unique rules of grammar and syntax that evolve and change over time.
The need for more qualified sign language interpreters has led to another great leap in AI applications that facilitate deaf individuals' access to sounds with new avatars capable of sign language. Although this technology is still in its initial stages, it’s exciting to see how it will evolve.
AI-Powered Assistive Listening Devices
Assistive listening devices such as hearing aids and cochlear implants have significantly advanced in recent years, propelled by AI innovations to enhance sound clarity through AI algorithms. By intelligently processing audio signals in real-time, hearing aids can filter out background noise, amplify speech frequencies, and optimize sound quality, ensuring a clearer and more immersive listening experience.
AI has also enabled levels of personalization through machine learning capabilities that adapt to individual preferences, learning from user interactions to fine-tune settings according to unique hearing profiles. Whether adjusting volume levels, equalizing frequencies, or optimizing directional microphones, AI-driven assistive devices offer tailored solutions that cater to each user's specific needs and preferences.
At the same time, cochlear implants have also leveraged this technology with advanced capabilities in noise reduction, sound localization, and speech enhancement, especially where background noise can interfere with speech perception.
AI in Education and Employment
Attending class lectures and gaining access to different class materials has become easier with AI-driven speech recognition and live transcription tools such as Nagish Live that facilitate real-time captioning and transcription of lectures, ensuring equal access to classroom instruction and promoting academic success.
In a work environment, AI-driven speech-to-text and text-to-speech technologies facilitate seamless communication, enabling deaf and hard of hearing employees to participate fully in meetings, conferences, and collaborative projects.

Looking Ahead
AI's rapid advancements are not merely improving accessibility but catalyzing a cultural shift, fostering awareness, and nurturing connections like never before.
By building bridges between deaf/hard of hearing individuals and hearing individuals, AI can play a pivotal role in creating a world where there are no communication barriers anytime and anywhere. From seamlessly transcribing in-person conversations to real-time captioning of online media, AI empowers deaf and hard of hearing individuals to navigate different settings in life with newfound ease and confidence.
It’s also another step towards redefining accessibility standards and fostering a world where everyone, regardless of their hearing abilities, can participate fully and engage meaningfully in all aspects of life, a key focus of our mission at Nagish.